The United States Federal Reserve (FED), at its last meeting, decided to keep interest rates unchanged. The fight against inflation continues, and despite being reduced compared to previous peaks, is still above the 2% target desired by the central bank. This decision has major implications for both the traditional economy and the volatile cryptocurrency market.
High inflation? Interest rates too
In recent months, the Federal Reserve did not move from its cautious position, opting to keep interest rates high to combat inflation. The current economic environment is complex, with moderate growth and a resilient job market that continues to demonstrate strength despite inflationary pressures.
Inflation is still an important variable in the equation. Although the FED has achieved some success in its reduction, the level above desired leaves the market on alert. For investors, especially in crypto, this means a period of uncertainty. Crypto assets, often seen as hedges against inflation, may not behave predictably in a scenario where monetary policy remains focused on strict inflation goals.
The aim is not only to stabilize prices, but also to prepare the ground for a future where interest rates can be adjusted downwards, without precipitating new inflationary outbreaks.
Inflation is a constant in many countries. The increase in consumer price indices has motivated monetary authorities to maintain interest rates high, as a containment measure, since the relationship between inflation and interest rates is intrinsic to monetary policy. When inflation is high, central banks tend to raise interest rates to reduce the amount of money circulating in the economy.
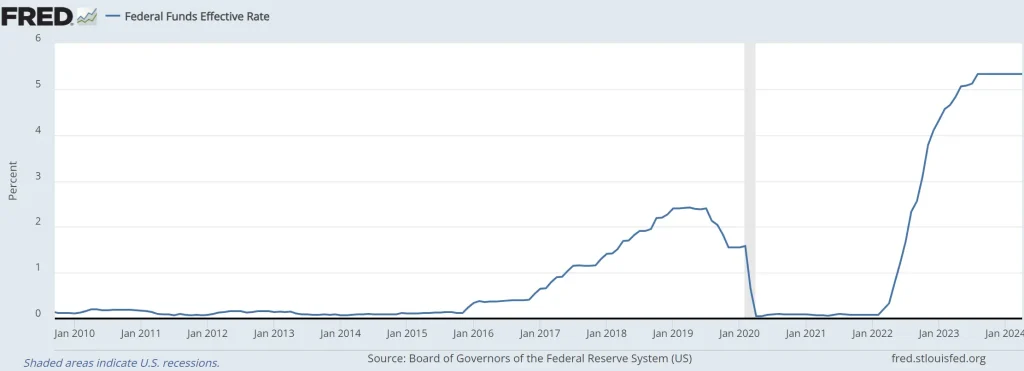
In the United States, FED faces the challenge of persistently high inflation, which has remained above the 2% stipulated as ideal for the country’s economic health. Therefore, the institution chose not to reduce interest rates, keeping them between 5.25% and 5.5%, the highest record since 2001. The concern about the continued hike in prices and the need for firmer action to ensure the return of inflation to more controllable levels are evident.
The FED’s plans
FED, the country’s central bank, has an important role in economic balance: adjusting monetary policies to keep inflation under control and encourage sustainable economic growth. So, interest rates are a tool for managing monetary policy. The FED’s current plan to slow inflation is to make credit more expensive. The aim is not only to stabilize prices, but also to prepare the ground for a future where interest rates can be adjusted downwards, without precipitating new inflationary outbreaks.
The US central bank announced that any future rate cuts will depend on a series of economic factors, including developments in inflation and the labour market. FED has emphasized the need to see clear signs that inflation is moving sustainably toward the 2% target before considering additional monetary policy adjustments.
But as long as the US Federal Reserve keeps rates stable, the market remains in a delicate position. In this scenario, it will continue to swing between hopes of a more relaxed monetary policy and the realities of an economy that is not yet ready to abandon its conservative approach to inflation.
And, to ensure that inflation reaches and remains at the desired percentage, the FED monitors several economic indicators, such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI), GDP growth, employment rates and wages. This data helps determine whether the measures in place are effective or whether adjustments are necessary.
The Federal Reserve is also paying attention to the impact of its policies on the global economy. In an increasingly interconnected world, Federal Reserve decisions also have international repercussions, influencing exchange rates, capital flows and economic conditions in other countries.
With inflation also exceeding the targets set by the Bank of England, interest rates have been adjusted higher than usual as a way of combating inflationary pressure. The purpose of this hike in the cost of borrowing is to discourage excessive consumption and speculative investment, which can further exacerbate inflation.
How does this affect investors?

These measures, although necessary to control inflation, have repercussions on citizens’ daily lives and investor strategies. Rising interest rates increase the cost of credit for purchasing properties, cars, and other financed goods. That said, the impact is direct on families’ purchasing power. For investors, this could mean a portfolio reassessment.
Impact on cryptocurrency investors
Crypto assets are particularly volatile and sensitive to general market sentiment. In periods of economic uncertainty, or when Federal Reserve policy suggests monetary rigidity, there may be a migration to safety, moving investors away from cryptocurrencies and toward assets considered safer. All of this could result in abrupt drops in cryptocurrency prices.
However, some schools of thought within the investment community see cryptocurrencies as a possible hedge against inflation, similar to gold. This is due to the decentralized nature and limited supply of many cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin. Theoretically, this makes them less susceptible to devaluation compared to fiat currencies, which can be inflated by government policies.
Impact on Forex traders
The foreign exchange market is extremely sensitive to central bank policies, as interest rates directly influence currency prices. It is one of the most important factors in determining exchange rates. When the FED raises rates, the dollar generally strengthens because investors are attracted to the higher yields offered by U.S. government bonds. This increases demand for the currency, valuing it in relation to others. On the other hand, if the Federal Reserve indicates a policy of reducing rates, the dollar could weaken as investors begin to look for higher yields in other currencies.
Therefore, any indication of a change in interest rate policy could greatly shake both traditional and digital markets. But as long as the US Federal Reserve keeps rates stable, the market remains in a delicate position. In this scenario, it will continue to swing between hopes of a more relaxed monetary policy and the realities of an economy that is not yet ready to abandon its conservative approach to inflation.