Understanding the Bitcoin Block Reward System
Transaction data are recorded in the bitcoin network in files called “blocks” and each time a block is discovered, a new bitcoin is minted and the miners receive compensations known as a “block rewards”. The rate of these bitcoins being created are cut in half every for years, limiting the supply contravening the entire financial concept of Quantitive Easing.
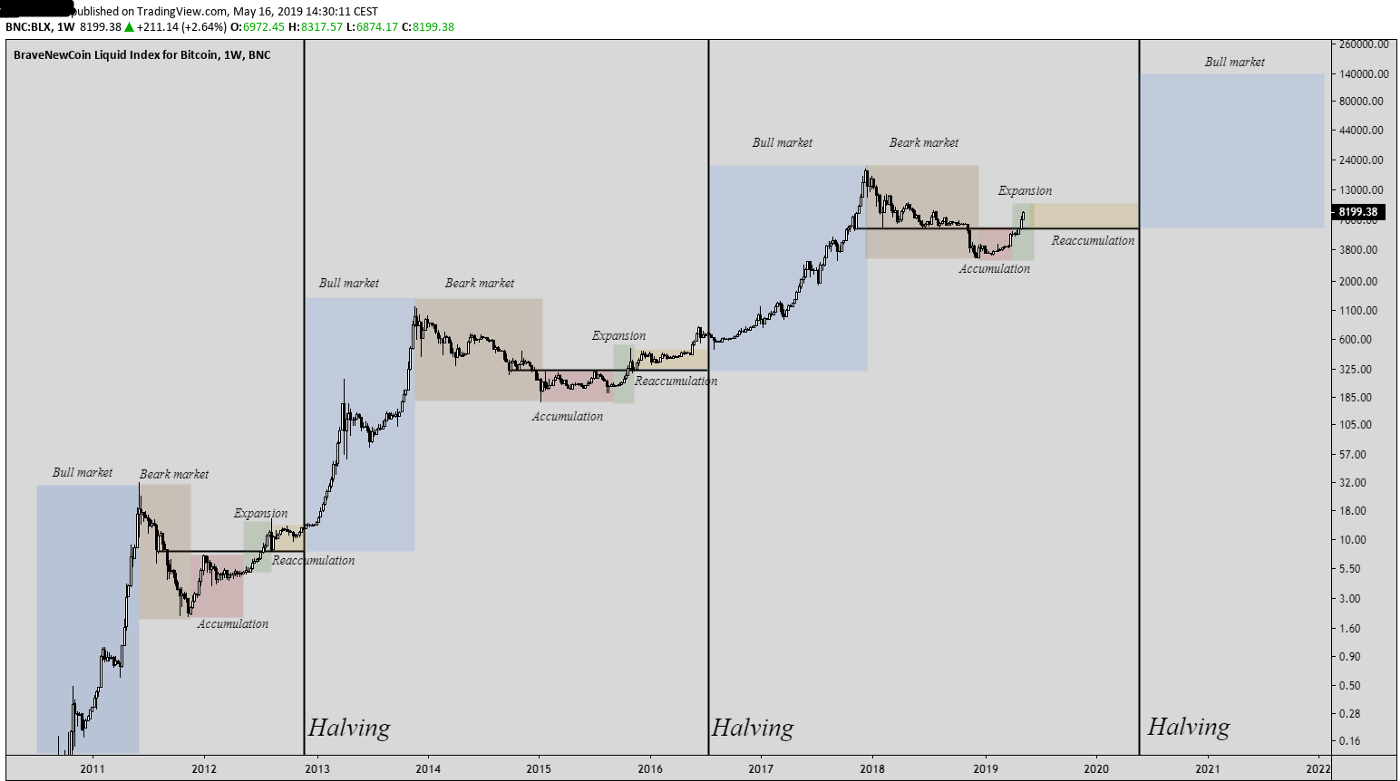
The Process of Bitcoin Easing
The act of shortening the supply and distribution of bitcoin is meant to reduce the reward size for miners and also control market inflation. The incentive for miners to purchase the equipment necessary (miners) to validate a transaction is offered by bitcoin known as block rewards. These miners are highly-functioning computers that specialize in performing computations that solve mathematical problems needed to validate transactions.
The reason miners validate transactions and add them to a ledger is so that the act of double spending doesn’t occur in the network. Double spending simply is when a false log is sent to the receiver notifying them that the transaction has occurred. Meanwhile, the sender didn’t actually send the amount the receiver is viewing. The sender of the double spent amount managed to duplicate their transaction sending one to the network and a false one to the receiver.
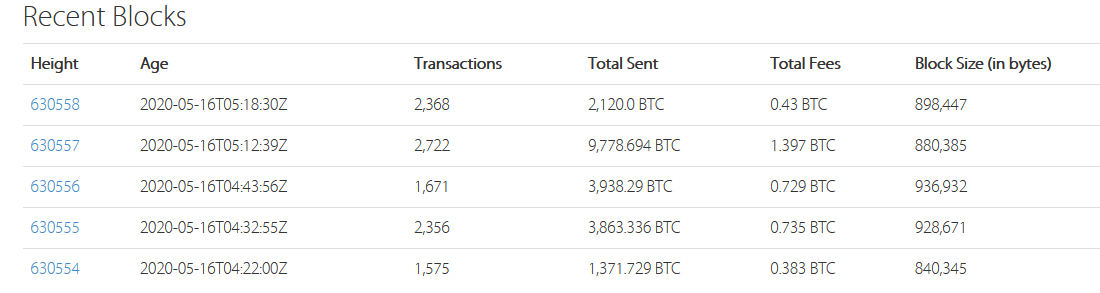
The act of mining bitcoin stops such attacks from happening. In order for a miner to successfully claim a block reward, they have to validate over 1MB worth of data onto the network. This means a few hundred thousand transactions must be confirmed and validated by that miner. The block reward is halved every 210,000 blocks (~4 years), known as the “bitcoin halving” and it so happens that we underwent it three days ago on May, 11th at block height 630,000. Every ten minutes a new block is filled with transactions and reference to the previous block, it is then moved onto the blockchain network where the next block will then attach to it with it’s recent transactions.
Only 21,000,000 bitcoins will ever be minted and these processes ensures that over time a sustainable, decentralized, and safe network is built.
Transactions on the Bitcoin Network
Transactions are authenticated and verified by miners so that malefactors don’t use methods such as double-spending to attack the network. The cost is emphasized on miners by the power they are consumer, the reward for 2020 is 6.25 BTC for 1 block. As a result of the bitcoin halving, the reward for transaction 1MB worth of transactions is 6.25 bitcoins as of May 11th, 2020.
By the year 2140 the creation of bitcoins will cease from occurring and miners will only be incentivized by transaction fees. In order for a miner to successfully validate a block-worth of data they will need a lot of computational power. The computers are used for solving hashes which in then return verify the transactions occurring in the bitcoin network. Having the luxury of having the necessary equipment to mine a block isn’t viable for many people, so communities have banded together and formed mining groups which work together to mine blocks and split rewards.
The halving shortens the encouragement of some miners for continuing as the reward is cut, but reducing supply and raising demand only equates to one thing, a bull market. In attempt to make the most of this market, daytrading cryptocurrencies have profited many who have taken advantage of such volatile swings. In terms of gather knowledge for such market trends, altsignals caters to both beginner and experienced traders who have interest in joining the cryptocurrency market and offers guides to those who want to build their education around the industry.