There are different consensus algorithms in the market as we have already shared with you in the past. Two of them include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). These two are used by Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH) respectively. However, there is a third and important consensus algorithm that is called Delegated Proof of Stale – or simply dPoS.
In this guide, we will share with you which are the main characteristics of the dPoS, how it works, which are the differences with other consensus algorithms and more.
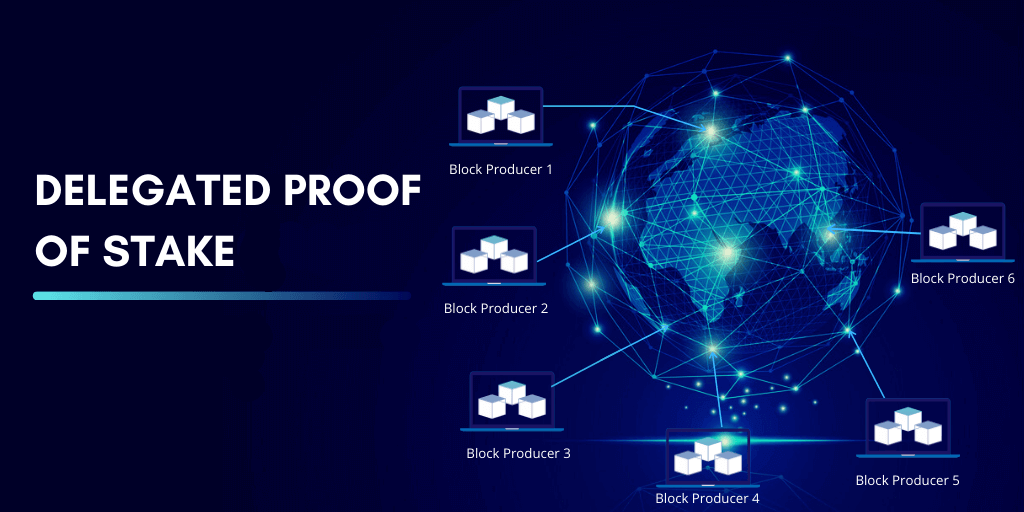
What is Delegated Proof of Stake (dPoS)?
Delegated Proof of Stake is a consensus algorithm that aims at making blockchain networks secure and efficient. Of course, this is the basic definition of how different consensus algorithms work and their main goal.
The main difference with other consensus algorithms is related to the fact that dPoS was created in order to use vote and election processes to improve decision making in different blockchain networks. Moreover, dPoS work in a more democratized way compared to other consensus algorithms.
One of the most popular blockchain networks using dPoS is EOSIO, which is the network that hosts the EOS digital asset. EOS is currently the largest cryptocurrency with a decentralized proof of stake consensus algorithm.
Indeed, the top 10 cryptocurrencies have the following consensus algorithms:
- Bitcoin: Proof of Work
- Ethereum: Proof of Work
- XRP: Ripple Consensus Algorithm
- Bitcoin Cash: Proof of Work
- Bitcoin SV: Proof of Work
- Litecoin: Proof of Work
- Binance Coin: Tendermint BFT
- EOS: Decentralized Proof of Stake
- Cardano: Proof of Stake
Each of these consensus algorithms works in a different way and would provide each of the networks with different characteristics and features. While PoW are considered to be highly secure, they may not be so efficient as Proof of Stake, which can be faster and cheaper to process transactions.
Meanwhile, the dPoS provides a new layer of democracy to the networks, which would be much better for the entire ecosystem that would be relying on a fairer way of handling transactions and information.
How Does the dPoS Consensus Algorithm Work?
The dPoS consensus algorithm works with witnesses and delegates. Users place the tokens they hold on the name of the candidates they chose to be representing them as delegates. Of course, the witnesses and delegates work in different ways from network to network.
Top-tier witnesses are those that will be receiving the rewards related to the network. The higher the number of tokens staked on a specific delegate the higher the rewards will be for the entity that is receiving the votes.
These delegates are voted in order to be those that will be governing the system, proposing changes, voting for new proposals and amendments to the blockchain and more. These are real entities that work so as to represent users on these blockchain networks.
While in PoS and PoW malicious behaviour can be easily punished, the same can happen with the dPoS consensus algorithm. Indeed, delegates are working on a daily basis to avoid being replaced by other delegates that could receive a higher number of votes. This is why these delegates are being reviewed on a daily basis.
The voting process never stops. If a witness misbehaves, then he will lose the vote of the community and eventually stop being considered one of the top delegates in the network. The surprising thing about dPoS is that any user, even those that hold small amounts of tokens, can start voting for their candidates and representatives.
This is why dPoS is considered to be a much more democratic process compared to other consensus algorithms that do not make it so easy for users to participate in their processes.
In PoW networks, users that have small amounts of computing power cannot have an influence on the decisions that are taken by the network. Indeed, it may be very expensive to have a voice on these blockchain networks, specifically in the biggest ones.
Meanwhile, PoS may require users to hold a large number of tokens before they can start staking their funds and participating in the network.
Conclusion
Delegated Proof of Stake is one of the most innovative consensus algorithms in the market. At the moment, EOS is the largest network with this system that is running and working. There are many advantages of the dPoS and also some disadvantages that blockchain developers need to take into account at the time of working on top of these networks.